WLAN Topologies AKA Service Sets:
I would like to talk about WLAN topologies or service sets which are not difficult to but very important to understand. 802.11 defines different topologies or service sets.
- BSS (Basic service set)
- ESS (Extended service set)
- IBSS (Independent basic service set)
- MBSS (Mesh basic service set)
- QBSS (QOS basic service set)
now look at few other abbreviations you might come across when we are talking about service sets.
- Station (STA) any device with WiFi radio, it could access point or your laptop, mobile etc
- BSSID (Basic service set ID)
- BSA (Basic service area)
- ESSID (Extended service set ID)
BSS (Basic service set):
Very simple topology or service set where we have only one access point (radio) serving, and one or more clients connected to it. Wi-Fi clients to the access point and communicate via access point as well rather than communicating directly.
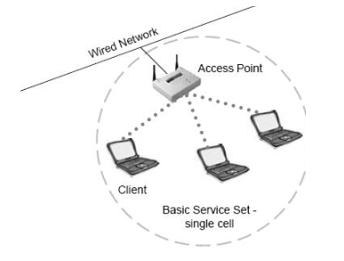
(Basic service set)
BSSID (Basic service set ID):
I have mentioned BSSID above and it’s important to understand what is BSSID. It is normally the MAC address of the radio. For client stations to connect to AP they need to connect via SSID so let’s suppose you have 2 APs with the same SSID so somehow you need to differentiate between both SSIDs. This happens via BSSID so every SSID will have different BSSID which can be shown in the Wireshark capture below.
It’s a beacon frame which is advertising information about BSS and BSSID can be seen in the advertisement as well.
![]()
(Beacon Frame)
Basic service area:
Basic service area is the physical area which is covered by one access point is called a basic service area. Client stations can maintain different data rates depending on the location with the reference of AP coverage area or BSA. BSA depends on surroundings, antennas, attenuation etc that’s why you will never see a perfect circle of BSA as its normally shown in different images on the internet.
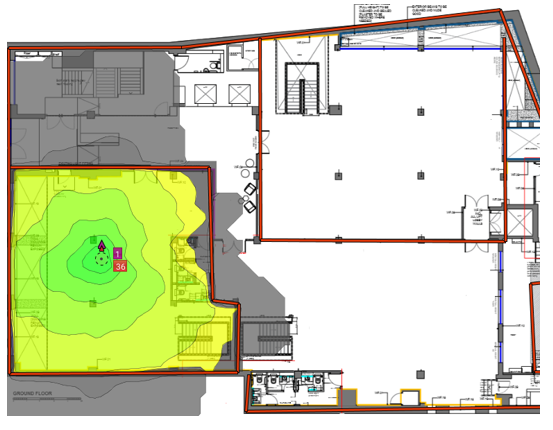
(Basic service area)
Extended service set (ESS):
Extended service set is an extended version of BSS where you have 2 or more BSS connected via distribution system medium (i.e LAN infrastructure). Let’s suppose in an office environment where multiple APs connected to same LAN and broadcasting one SSID called as Office. So, devices can connect with Office SSID in one basic service set and move from one BSA to other BSA while keeping the same connectivity such as SSID and IP address etc.
Its also good practice to have some overlap in between different BSAs so devices can roam from one BSS to another.
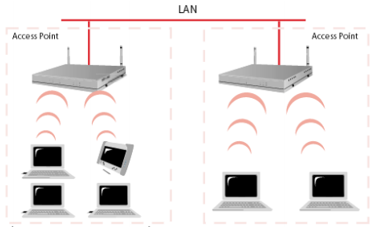
(Extended service set)
ESSID OR SSID: logical name of the extended service said can be called as ESSID and it is also called as SSID. Just a point to mention if you have more then 1 SSIDs it means you will have multiple BSSIDs. Every SSID will have its own BSSID.

(Multiple BSSIDs within ESS)
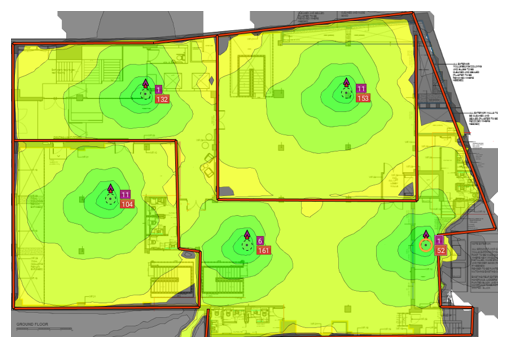
(multiple BSS making ESS)
IBSS (Independent basic service set) or Adhoc Network:
Independent basic service set is the topology where an access point is not involved. Client stations create a wireless network independently with each other. All clients communicate with each other each other directly as a peer to peer connection and only one client can talk at a time.
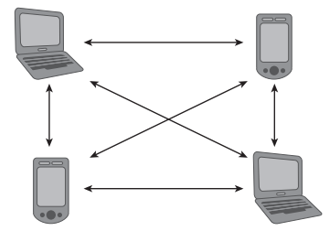
(Independent service set)
There is a couple of points to be noted in the independent service set. The first station who initiate the network will create virtual BSSID and for stations to communicate they will have to use the same channel.
MBSS (Mesh basic service set):
In 2012 802.11 defined mesh topology. Mesh network can be used where wired network is not possible and Aps can not be connected to Wired network to create ESS. The mesh function is used to provide wireless distribution to the network traffic.
Access point creates a wireless mesh connection to the nearest access point available towards Wired infrastructure. One or more Aps can be connected to Wired network and rest can connect to each other wirelessly.

(Mesh Network)
QBSS (QoS basic service set):
There is nothing fancy about this BSS but very important BSS. It’s simply QoS implementation in a BSS. Every new enterprise access points will have QoS capabilities but some legacy equipment might not have QoS capability.